Valves and taps are devices designed to regulate, open or close the flow of liquid or gas in a pipeline. They should be made of brass, gun metal or other corrosion resisting alloys. They may be made by casting metal into moulds or by hot pressing metal between dies.
Some of the more common valves and taps and their uses are given in the table below.
Valve / Tap |
Use |
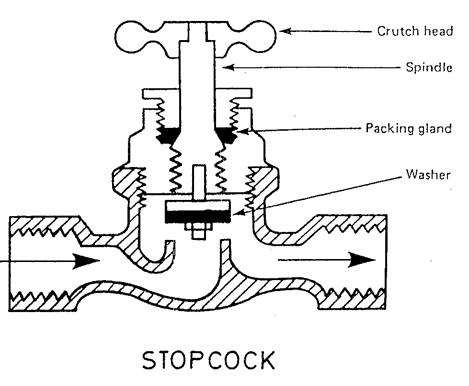
Stopcock |
Used on incoming high pressure water mains. |
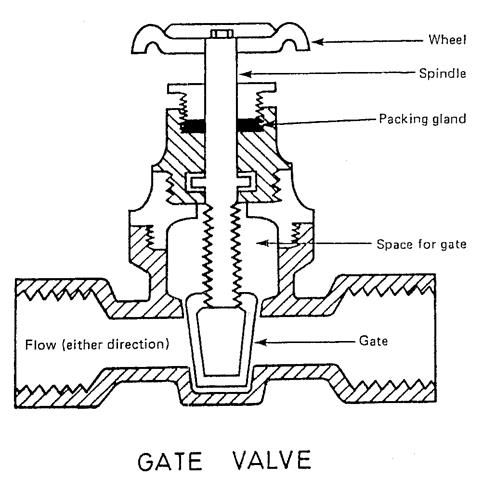
Gate valve |
Used on low pressure pipework. |
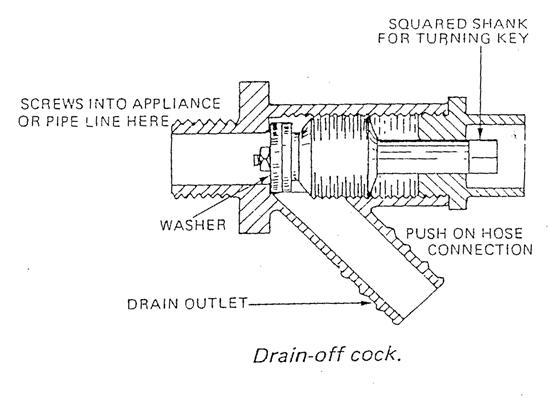
Drain off cock |
Used to drain pipework |
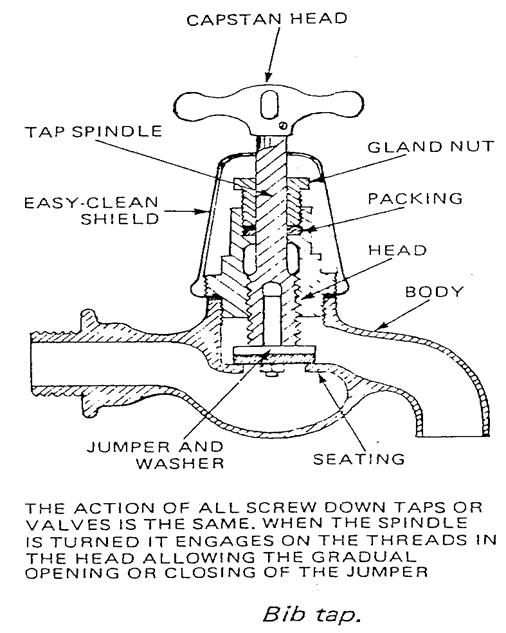
Bib tap |
A well mounted tap primarily used over sinks and also for outdoor use. |
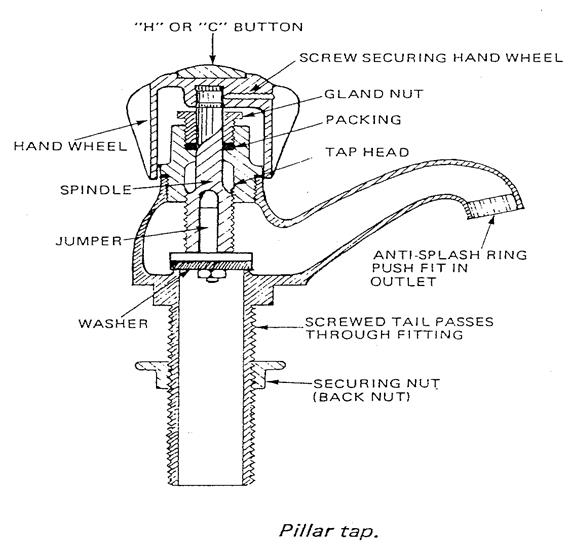
Pillar tap |
Used on sinks, wash hand basins and baths. |
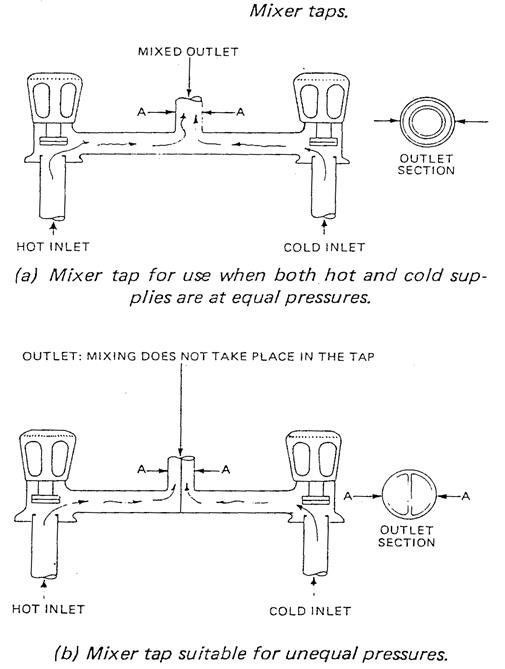
Mixer taps |
A tap in which hot and cold water are delivered through a common spout. Used on sinks, wash hand basins and baths. |
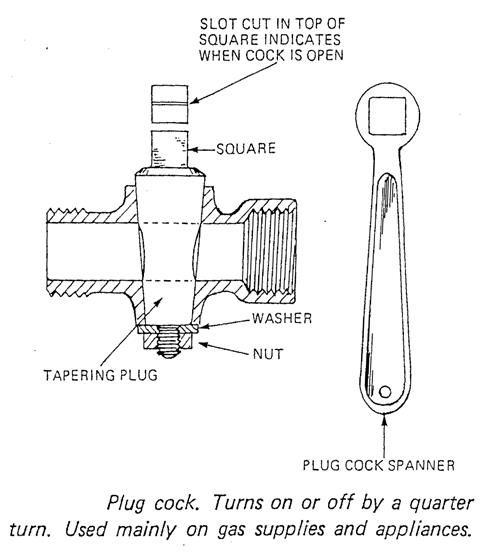
Plug cock |
A quick closing valve used mainly on gas installations. |
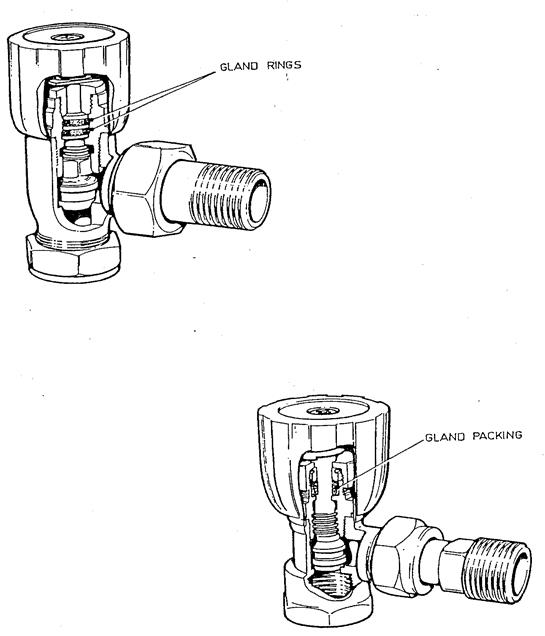
Radiator valves |
Used to control the flow of water to and from radiators. |
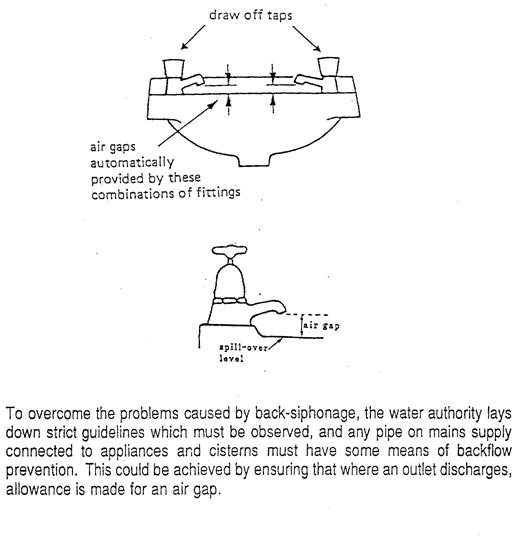
The backflow of water by siphonic action from an appliance or storage cistern into the pipe feeding it, thus contaminating the water supply. To overcome the problems caused by back-siphonage the water authority lay down strict guidelines which must be observed and any pipe on mains supply connected to appliances and cisterns must have some means of backflow prevention. This could be achieved by ensuring that where an outlet discharges allowance is made for an air gap of at least that shown in the chart.
Internal Pipe Diameter |
Vertical distance (air gap) between outlet and highest possible water level |
Up to 14mm |
20mm |
If a specified air gap cannot be achieved some other means of backflow prevention must be catered for. In the case of hose pipes and shower hoses connected to the mains supply a double check valve assembly or similar arrangement such as a check valve followed by an anti-vacuum valve must be used.
Source: http://local.ecollege.ie/Content/APPRENTICE/liu/Plumbing_notes/Valves_Taps_M2_U9.doc
Web site to visit: http://local.ecollege.ie
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes