Chapter 6 The Influence of Corporate Strategy on an Organization
LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Explore the relationship between a corporate parent and its business units. |
1. Relationship between a Corporate Parent and its Business Units
1.1 Introduction
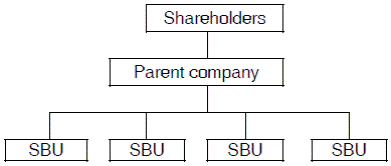
1.1.1 Many organizations consist, essentially, of a number of strategic business units (SBUs) and a corporate parent. Each SBU has its own products, with which it serves its own market sector, and its managers are, to a greater or lesser extent, responsible for its overall success (or failure).
1.1.2 In very large organizations, SBUs may be grouped into divisions, with divisional managers providing an intermediate level of management between the SBU and the corporate parent.
1.1.3 Since most groups of companies do have an active parent company, making strategic decisions, there must be an acceptance that parent companies can add value.
1.2 Three rationales for adding value
1.2.1 There are three different ways of arguing that a parent company can add value to a group. Each different argument is based on a different view of the role of the parent company. A parent company can perform any one of the following roles for the group:
(a) Portfolio manager
(b) Synergy manager
(c) Parental developer
(a) Portfolio manager
1.2.2 This view of the role of the parent is that the parent acts as a corporate manager, operating on behalf of the shareholders. In this role, the parent buys and sells SBUs (or discontinues SBUs), depending on the corporate strategy choices that it makes and as opportunities arise. However, the parent company has a ‘hands-off’ approach to the management of the businesses of the group. Each SBU is managed independently, by its own managers, without any interference or advice from the parent.
1.2.3 When it performs this role, the parent company is managing a portfolio of investments, in much the same way as an investor might manage a portfolio of shares in different companies.
1.2.4 As far as the parent is concerned, it does not matter what businesses the SBUs are in. They can be totally different investments. All that matters is the size of the return provided by each SBU.
1.2.5 In this role, the parent company adds value only if it can manage the portfolio of businesses better than its own shareholders could if they were investing directly in the stock market. It can do this by:
(a) identifying and acquiring under-valued businesses
(b) encouraging under-valued businesses to improve their management and performance, so that their value increases: the managers of each SBU might be given financial performance targets that the parent expects the SBU to achieve
(c) selling off over-valued businesses, and
(d) selling off under-performing businesses that fail to improve.
1.2.6 The parent should also try to keep its own operating costs as low as possible. Head office will therefore have a very small staff.
(b) Synergy managers
1.2.7 A parent might perform the role of synergy manager, by identifying opportunities for synergies across the group. Synergies might exist when:
(a) two or more SBUs in the group are able to share the same resources, and so reduce operating costs
(b) two or more SBUs in the group can share a joint activity, and so reduce operating costs
(c) two or more SBUs can share skills and competences that exist across their businesses, so that skills and competences that are learned and acquired in one SBU can be taught to other SBUs.
1.2.8 Opportunities for synergy and cost savings can exist only when the SBUs have something in common that they can share. A synergy manager role cannot be performed by a parent company of a widely-diversified group of SBUs.
1.2.9 There are also difficulties for a parent company in performing a synergy manager role successfully, even when opportunities for synergies do exist.
(a) The costs of operating the parent company might exceed the benefits of the synergies it is able to find.
(b) The parent might have difficulty in overcoming the self-interest of the managers of the SBUs and persuading them to co-operate with each other.
(c) There might be cultural differences between the SBUs, which make it very difficult for the SBU managers to co-operate successfully.
(d) Synergy management cannot be successful unless the management of the parent has the determination to make synergies work. Where necessary, this will mean intervening in the management of the SBUs whenever necessary, and ‘forcing’ them to co-operate to achieve the synergies.
(c) Parental developers
1.2.10 A parental developer is a corporate parent that brings some of its own skills to bear on SBUs to help them to develop and add value. (This differs from synergy management, where the corporate parent looks at how sub-units might help each other. Here, the corporate parent teaches the SBUs some of its own competences.)
1.2.11 For example, a corporate parent might have very good international marketing skills and these skills can be used to add value to a SBU that is attempting to sell its goods in other countries.
1.2.12 Parental developers must be clear about the distinctive skills, capabilities and resources that it has that can add value for an SBU. A ‘parenting opportunity’ is a SBU that is not fulfilling its potential and where the parent has particular skills or competences that can help to the SBU to improve.
1.3 Ways in which parents can destroy value
1.3.1 Parent companies can destroy value rather than create it. A parent destroys value when the benefits it provides to the group are less than the costs of operating the parent.
(a) When a parent company acts as a portfolio manager, its selection of SBUs for the group’s business portfolio might be no better – or even worse – than the choices that could have been made by its own shareholders if they had been making the business investments directly.
(b) When a parent acts as a synergy manager, it may fail to realise enough synergies, for the reasons explained earlier.
(c) When a parent acts as a parental developer, it might try to use its skills and competences where they bring little or no benefit to the SBU. There has to be a good ‘fit’ between the parent and the SBU.
2. Corporate Strategy Selection and Portfolio Models
2.1 Introduction
2.1.1 Corporate strategy selection involves making decisions about which businesses to invest in, and which businesses to divest, in order to create a suitable portfolio of businesses that should enable the company to achieve its strategic objectives.
2.1.2 A number analytical methods have been developed to help managers assess which SBUs they should have in their business portfolio. Collectively, these methods are known as portfolio analysis models.
2.1.3 Portfolio analysis is simply an approach to analysing:
(a) markets, and their future potential for growth and profitability, and
(b) the position of a business entity within those markets.
2.1.4 The purpose of this analysis is to make decisions about the most suitable portfolio of businesses. The selected portfolio should then become the established corporate strategy for the company.
2.1.5 All portfolio models are based on the assumption that the optimal corporate strategy is to invest in a range of different businesses and products. It would be very risky to rely on just one product, or even on a limited range of products, because of the risk that these might be unprofitable or might go into decline at the end of their life cycle.
2.1.6 The portfolio models described in this chapter are:
(a) the Boston Consulting Group matrix (BCG matrix).
(b) the directional policy matrix.
(c) the parenting matrix (Ashridge Portfolio Display)
(d) the public sector portfolio matrix.
2.2 Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG matrix)
2.2.1 The Boston Consulting Group developed a product-market portfolio for strategic planning. It allows the strategic planners to select the optimal strategy for individual products or business units, whilst also ensuring that the selected strategies for individual units are consistent with the overall corporate objectives.
2.2.2 The objective of the matrix is to assist with the allocation of funds to different products or business units.
2.2.3 The matrix is a 2 × 2 matrix.
(a) One side of the matrix represents the rate of market growth for a particular product or business unit.
(b) The other side of the matrix represents the market share that is held by the product or business unit.
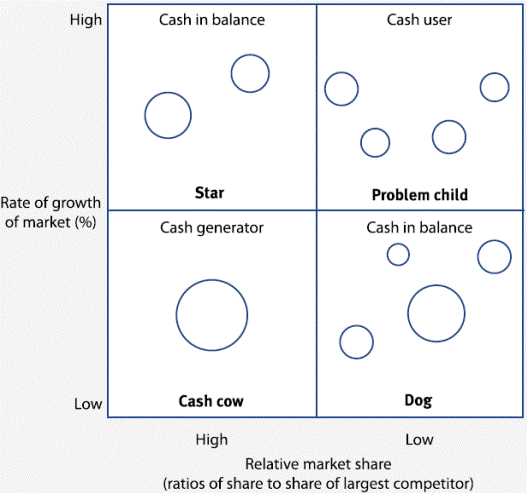
2.2.4 Market growth. The mid-point of the growth side of the matrix is often set at 10% per year. If market growth is higher than this, it is ‘high’ and if annual growth is lower, it is ‘low’. It should be said that 10% is an arbitrary figure.
2.2.5 In the BCG matrix, market share is measured as annual sales for the product as a percentage or ratio of the annual sales of the biggest competitor in the market. The mid-point of this side of the matrix represents a situation where the sales for the firm’s product or business unit are equal to the annual sales of its biggest competitor. If a product or business unit is the market leader, it has a ‘high’ relative market share. If a product is not the market leader, its relative market share is ‘low’.
2.2.6 The individual products or business units of the firm can be plotted on the matrix as a circle. The size of the circle shows the relative money value of sales for the product. A large circle therefore represents a product with large annual sales.
2.2.7 Interpretation of the matrix.
The primary assumption of the BCG matrix is that the higher an organisation’s market share, the higher its profitability and the lower its costs due to economies of scale, the experience curve and improved bargaining power.
On this basis, products are placed into one of four subdivisions.
(a) Cash cows – with a high relative market share in a low growth market and should be generating substantial cash inflows.
(b) Stars – which have a high relative market share in a high growth market and may be in a later stage of their product life cycle. A star may be only cash neutral despite their strong position, as large amounts of cash may need to be spent to defend an organisation’s position against competitors. Stars represent the best future prospects.
(c) Problem children or question marks – characterised by a low market share in a high growth market. Substantial net cash input is required to maintain or increase market share.
(d) Dogs – with a low relative market share in a low growth market. Such a product tends to have a negative cash flow, that is likely to continue.
2.2.8 An organisation would want to have in a balanced portfolio:
(a) cash cows of sufficient size and/or number that can support other products in the portfolio
(b) stars of sufficient size and/or number which will provide sufficient cash generation when the current cash cows can no longer do so
(c) problem child that have reasonable prospects of becoming future stars
(d) no dogs or – if there are any – there would need to be good reasons for retaining them.
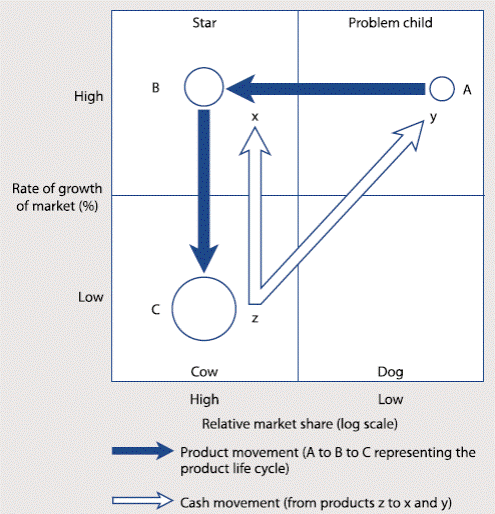
2.2.9 Strategic movement on the BCG matrix:
A product’s place in the matrix is not fixed for ever as the rate of growth of the market should be taken into account in determining strategy.
(a) Stars tend to move vertically downwards as the market growth rate slows, to become cash cows.
(b) The cash that they then generate can be used to turn problem children into stars, and eventually cash cows.
2.2.10 The ideal progression is illustrated below
2.2.11 Using the BCG matrix:
Categories |
Strategy |
Cash cow |
|
Stars |
|
Problem children / question mark |
|
Dog |
|
2.2.12 |
Example 1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A company produces five different products, and sells each product in a different market. The following information is available about market size and market share for each product. It consists of actual data for each of the last three years and forecasts for the next two years.
In the current year, the market share of the market leader, or the nearest competitor to the company, has been estimated as follows:
Required: (a) Using the Boston Consulting Group model, how should each of these products be classified? Answer: A cash cow is a product in a market that has little or no growth. The market share, however, is normally quite high, and the product is therefore able to contribute substantially to operational cash flows. Product 2 appears to be a cash cow. In the current year its market share was over 53%, and it is the market leader. A dog is a product in a market with no growth, and where the product has a low share of the market. Dogs are likely to be loss‐making and its cash flows are probably negative. Product 4 appears to be a dog. The total market size is not changing, and the market share for Product 4 is only about 3%. This is much less than the 29% market share of the market leader. A question mark is a product with a fairly low market share in a market that is growing fairly quickly. Product 1 appears to be a question mark. The total market is growing quite quickly, but the market share of Product 1 is about 4% and this is not expected to change. Product 5 also appears to be a question mark, for the same reason. The company should decide on its strategy for the products it will sell.
For all the products (with the exception of Product 4, if this is abandoned) the company should also consider ways of making the products more profitable. Techniques such as value chain analysis might help to identify cost savings. |
Question 1 In order to regain a competitive position Adrian Reed, the Managing Director of McGeorge Holdings, has been advised to reduce the range of products and the product lines. Advisors have suggested that a cut back in the product mix by about 20% could increase profits by at least 40%. Reed is keen to implement such a product divestment strategy but he fears that this cutting back could alienate customers. He needs to know which products need to be removed and which products are important to the survival of the company. He is unhappy about the overall performance of his company's activities. Benchmarking has been recommended as a method of assessing how his company’s performance compares with that of his competitors. Required: (a) Using appropriate analytical models discuss how Adrian Reed might select the products to be removed from the portfolio as part of his product divestment strategy. |
2.3 Shell directional policy matrix
2.3.1 The Shell directional policy matrix is another portfolio model. It can also be called the ‘attractiveness matrix’.
2.3.2 Like the BCG matrix, the directional policy matrix is used to place products or business units in a grid. It is a 3 × 3 matrix. This allows products to be treated with a more graduated approach than the 2 × 2 BCG matrix.
2.3.3 Industry attractiveness. One side of the grid represents the attractiveness of the business sector or market. Indicators of market attractiveness include:
− Profitability
− Growth prospects
− Strength of competition
− Market size
− PESTEL issues (opportunities and threats in the business environment)
− Customer and supplier pressure
− Entry barriers
− Business risk
2.3.4 Competitive strength. The other side of the grid represents business sector or market strength compared to the competition. Indicators of competitive strength include:
− Market share
− Managerial ability
− Low cost base
− Successful innovation
− Strong finance
− Know-how
− Brand
2.3.5 The company’s position in the business sector, which is categorised as Strong, Average or Weak.
2.3.6 The strategic decision about what to do with the product in the future is guided by the position of the product in the grid.
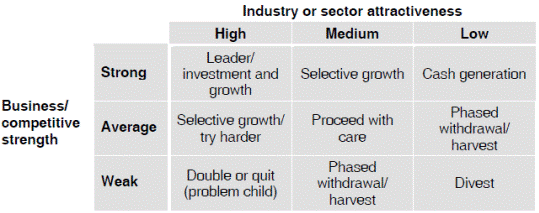
2.3.7 Using the directional policy matrix
(a) A strategy of immediate withdrawal (divest) from the market is indicated only when the industry or sector attractiveness is low and the entity has a weak position in the market.
(b) A strategy of phased withdrawal may be appropriate to maintain the entity’s reputation with customers. Presumably, the product or business is not cash negative, which means that there is no need for immediate withdrawal. However, it would be inappropriate to invest further in these products or business sectors.
(c) When an entity has a strong position in its market, its strategy should be based on maintaining or improving its position. However, if future prospects for the business sector are poor, the entity should probably treat its product as a ‘cash cow’.
(d) When an entity has an average position in a business sector with attractive future prospects, its strategy should be aimed at competing more effectively.
(e) Strategy selection is more difficult when an entity has a weak position in a sector with strong growth prospects, or an average position in a market with average prospects. The policy guidelines – ‘double or quit’ and ‘proceed with care’ should indicate the existence of a strong element of risk in strategy selection.
2.4 The parenting matrix (Ashridge Portfolio Display)
2.4.1 The Ashridge Portfolio Display matrix can be used to assess the role of the parent company in the strategic management of the business units in the group.
2.4.2 If a parent company becomes involved in the management of the business unit, it might add value, through improvements in operating efficiency, providing synergies, building competences in the business unit, providing expertise, managing risks at a group level (e.g. financial risk management) and providing corporate vision.
2.4.3 However, a parent might also create harm and destroy value by adding costs with no benefits, and creating extra bureaucracy and delay.
2.4.4 The matrix is based on the view that there is degree of ‘fit’ between a parent company and a business unit (subsidiary). When the fit is high, the parent company understands the business unit well.
2.4.5 There is also a degree of opportunity for a parent company to add value to a business unit.
2.4.6 The opportunity for a parent to become involved in a business unit, and add value, therefore depends on:
(a) the degree of fit between the parent and the business unit (the capacity of the parent to add value) and also on
(b) the existence of opportunities for the parent to add value.
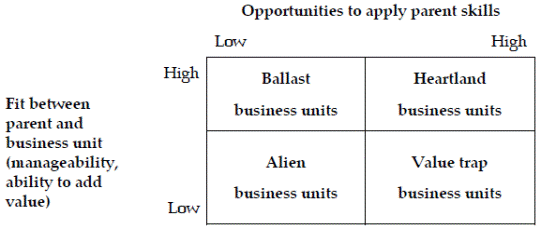
2.4.7 Interpretation:
(a) Heartland (心臟地區) business units. These are SBUs to which the parent can add value without any danger of doing harm to the SBU. These SBUs should be at the core of the parent’s future corporate strategy.
(b) Ballast (穩定) business units. These are SBUs that the parent company management understand well, but the parent can do very little to add value to the SBU. These SBUs could just as easily operate as an independent company as a business unit within the group, because it obtains no value from being within the group. If they are to be included within the future corporate strategy of the group, they should be managed with a ‘light touch’ by the parent.
(c) Value trap business units. These are SBUs where there are opportunities for the parent company to add value. However, there is a risk that in trying to add value, the parent might actually do the SBU more harm than good. These business units should only be included in the future corporate strategy of the group if the parent company’s management is convinced that the SBU can be moved from the ‘value trap’ to the ‘heartland’ category of business units. For this to happen, the parent must be able and willing to gain a better understanding of the business. Sadly, too many parents think they know best, and do harm to the business.
(d) Alien business units. These are SBUs that are ‘misfits’ within the group. The parent company can do little or nothing to add value for the SBU, and the SBU does not fit in well with the other businesses of the group or the culture of the parent. A exit strategy is advisable for these SBUs and the corporate strategy should be to dispose of them.
2.4.8 You might be wondering how a parent company could add value to an SBU when there is a risk that it could also do harm. An example would be the case of a parent company that has very good international marketing skills. It could use these skills to help an SBU to sell its goods in other countries for the first time. However, a strategy of selling goods to other countries might be the wrong strategy for the SBU. So although the parent would be using its skills to help the SBU, it would also be causing harm.
2.5 Public sector portfolio matrix
2.5.1 The public sector portfolio matrix is a portfolio selection model for public sector services, which can be used by individual public sector entities to choose the projects in which they should invest their available funds. It is a 2 × 2 matrix.
(a) One axis shows the organisation’s ability to serve the public effectively. A high ability to serve effectively means that it is well-funded at the moment.
(b) The second axis looks at political attractiveness in terms of whether or not the service can gain public support and so whether it should attract funding in the future.
2.5.2 The matrix produces four types of public sector service.
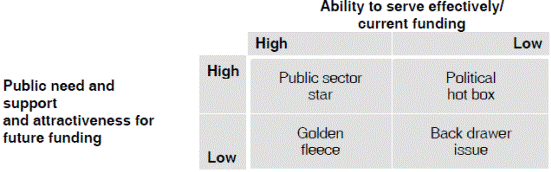
2.5.3 Interpretation:
(a) Public sector stars perform well and are likely to well-funded at the moment. They are also attractive to the public and meet a strong public need. Public sector services in this segment should attract more funding in the future. However, it can be difficult to find examples for this segment, if only because members of the public often have very different experiences of public services and would disagree about how well they perform.
(b) Political hot boxes are very popular but deliver a service that is perceived as poor. They are probably services that are too new and inadequately resourced to be delivered effectively. These services are similar to question marks in the BCG matrix. A strategic decision has to be taken about whether more funding should be given to them in the future. Some national health services might be perceived to fall into this category.
(c) Golden fleece services are well-resourced and are being delivered effectively. However, they are no longer meeting a strong public need. They are likely to be viewed as over-staffed and a drain on the public funds, and could be at risk of budget cuts in the future.
(d) Back drawer services have a low priority with the public, have no political support and are not delivered effectively, possibly because of poor funding. If possible they should be abandoned.
2.5.4 Weaknesses:
(a) An obvious weakness to this portfolio model is that the assessment of ‘meeting the needs of the public’ could be subjective. How is a distinction made between services that appear to meet a public need and those that do not? The public need cannot be measured reliably by public opinion, because public opinion is changeable.
(b) Another weakness is that effectiveness in delivering the service often depends on the level of public funding that the service is given. A more effective service is likely when funding is adequate. The only difference between a public sector star and a political hot box might therefore be the current level of funding and its implications for the effectiveness of the service.
Source: https://hkiaatevening.yolasite.com/resources/P3BANotes/Ch6-InfluenceCorporateStrategy.doc
Web site to visit: https://hkiaatevening.yolasite.com
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes